Flood And Drain System: What Is It & How Does It Work?
A flood and drain system is a hydroponic method that involves regular flooding and draining of a nutrient solution to the plants. This technique is familiar to many beginners in hydroponics.
However, how does this system work? This is a common question for many growers. Of course, after reading the article below, you will know how to build a flood and drain hydroponic system for yourself. Read now.
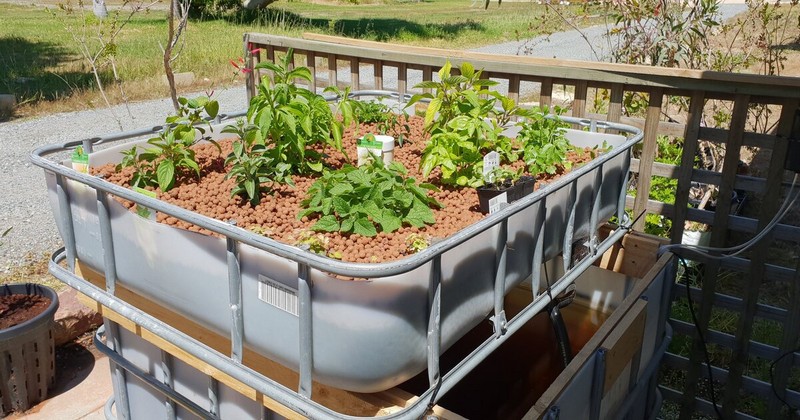

What Is Flood And Drain?
The flood and drain, or Ebb and Flow, system involves flooding and draining nutrient solutions at regular intervals. This system works in two phases:
- During the Flood phase, the nutrient solution flows over the plant roots, providing the necessary nutrients.
- In the Drain phase, the solution drains back to the reservoir.
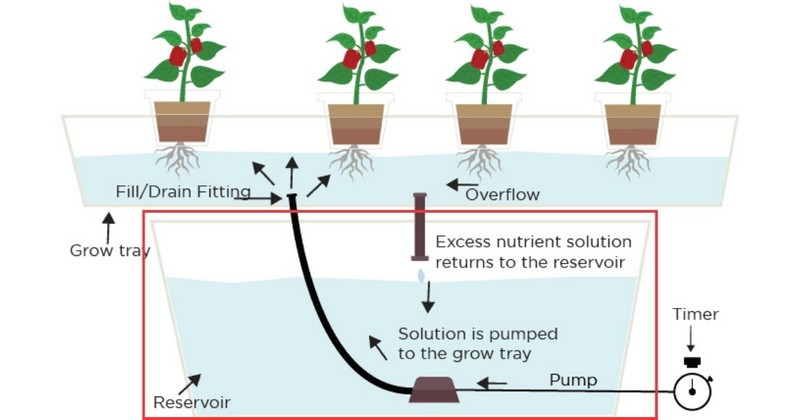
Unlike deep water culture, flood and drain systems do not permanently keep a plant's roots in the nutrient solution. In the flowering and fruit-bearing stages, growers tend to let the roots dry out between irrigation cycles, but the plant still responds well.
How The Ebb And Flow System Works
You may notice various containers or one container where plants are arranged on a grow tray or growing bed. Then below these containers is a timer. The timer controls the water-pumping cycle.
Once the timer goes on, the submersible fountain pump starts pumping nutrients and water. The nutrient solution then flows to the above container (or grow tray), soaking the plants' roots until they reach a certain water limit.
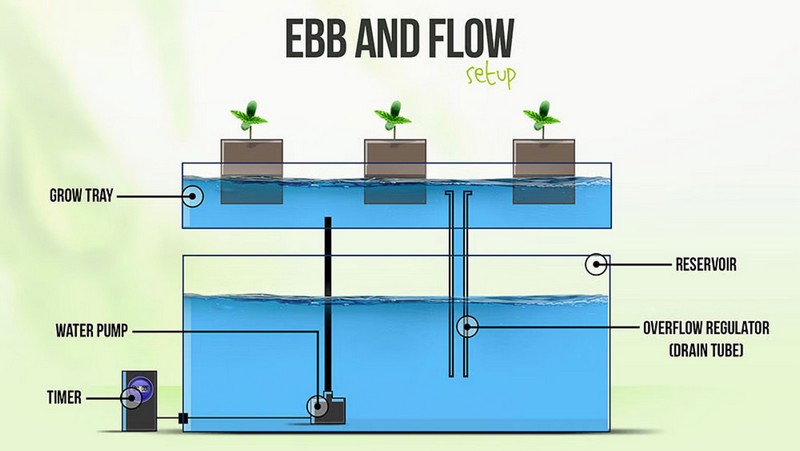
At the set level, there is a continuous circulation of nutrient water in the system for a period. The overflow tube is instrumental in maintaining the standard water level and preventing nutrient water from spilling out of the reservoir during circulation.
Once the timer goes off, the pump stops nutrient liquid from flowing in tanks. However, it begins draining back into the water reservoir through the drainage system.
See more: wick hydroponic system.
Materials For Building The Ebb And Flow Hydroponics
The system generally has two main parts – the reservoir and the plant tray. Let's analyse the reservoir first.
The Reservoir
Reservoir in an ebb and flow hydroponics system is the core component of operation.
It's a storage tank with the nutrient solution your plants need to thrive. Below are the 3 most important components of this material you need to be aware of.
Nutrient Solution Reservoir
One of the essential parts of any hydroponic system is the reservoir. This includes water and nutrients adjusted to your plant's demand. Normally, 1 reservoir is enough for most flood and drain systems.
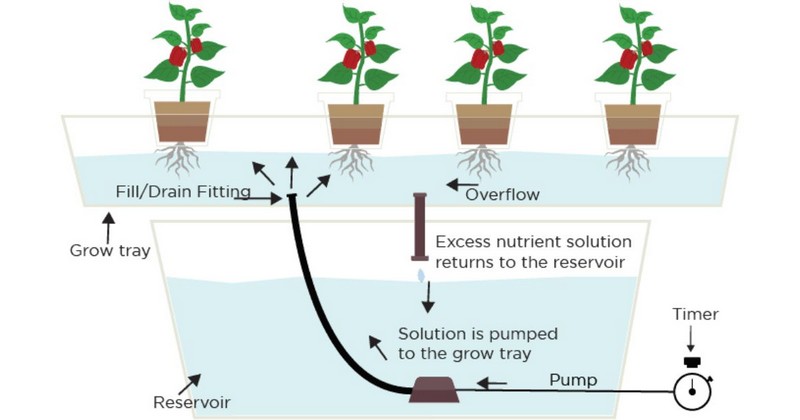
If your structure is large, the reservoir must also rise up, or you need some extra reservoirs to grow enough nutrients for more plants.
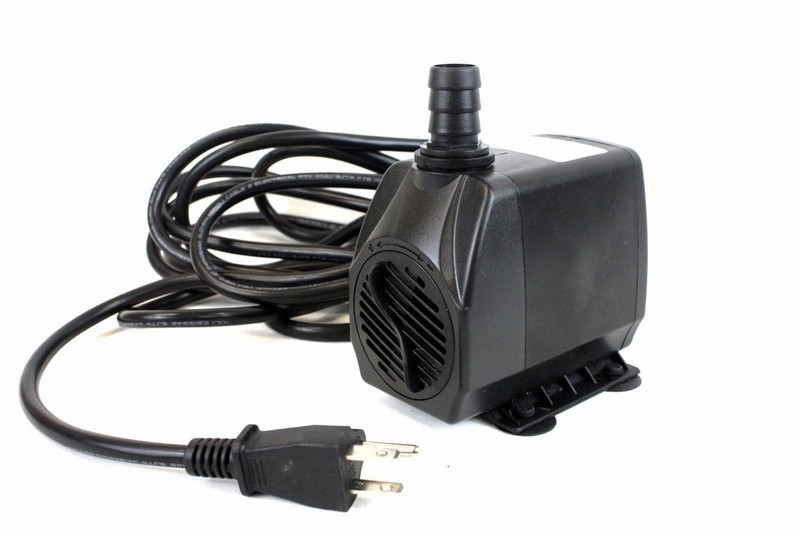
Submersible Pump
Like the NFT hydroponics, a flood and drain setup has a pump, either an inline or submersible pump, to transport water to the plants. A submersible pond or fountain pump is the heart of the Ebb & Flow system.

Timer
A timer controls the watering process's time, ensuring the plants receive enough nutrients.
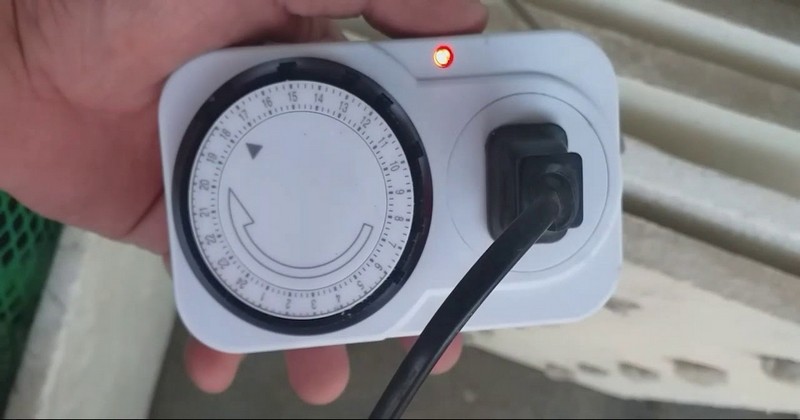

There are 2 different timers:
- Mechanical timers are simpler and more affordable but offer less flexibility in scheduling.
- Digital timers provide more precise control over the watering schedule with multiple on/off cycles throughout the day and night.
Before purchasing timers, look for the following features:
- Multiple outlets (if controlling multiple pumps).
- Battery backup (in case of power outages).
- User-friendly interfaces.
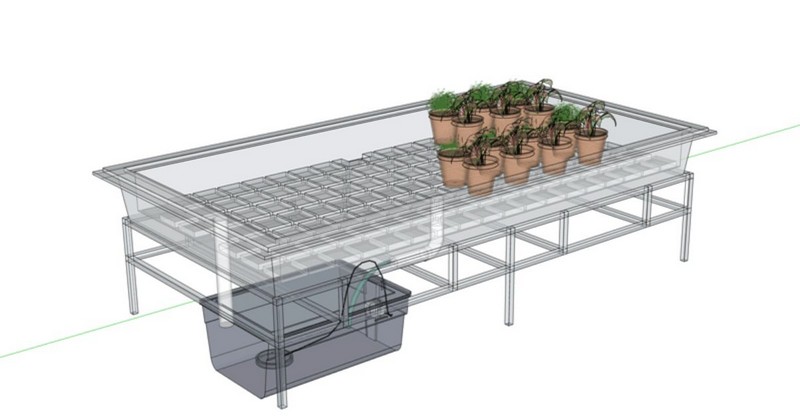
The Grow Tray
A grow tray, or flood table, is a container used in hydroponic systems to hold plants and their growing medium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, and their main function is to provide support and a platform for plants to grow without soil.
Container
A container or plant bucket is where the plant matures. It can be one big container/tray or some small ones in a flood and drain system.
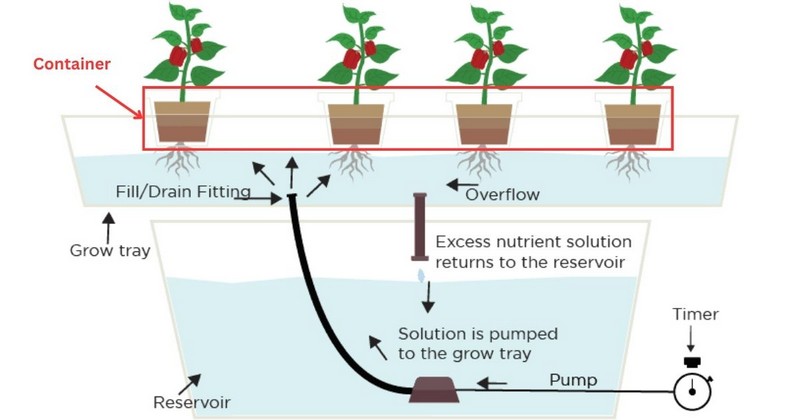
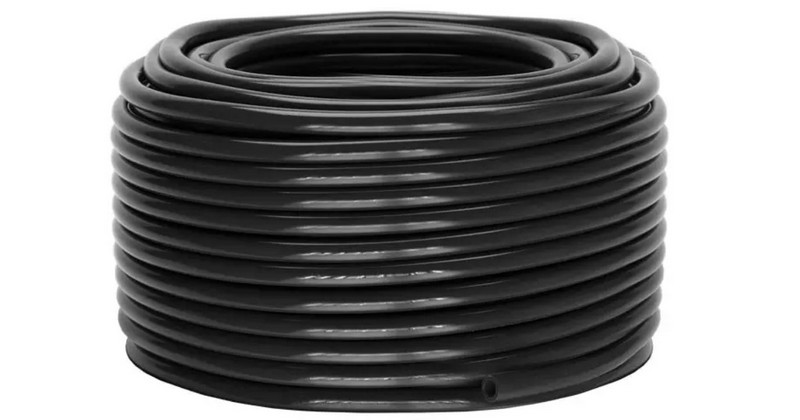
Tubing
The function of the tool is to connect the reservoir to the system to transport water in and out of the system. Regarding materials, there are 2 types:
- Food-grade plastic. Commonly used material due to its affordability, flexibility, and resistance to nutrient solutions. Options include PVC, polyethylene, and polypropylene.
- Silicone. More expensive but offers superior durability, heat resistance, and non-leaking properties—a good choice for larger systems or harsh environments.

Overflow Tube
The overflow tube has two primary functions.
Firstly, it helps regulate the nutrient solution level in the container. Secondly, it ensures the nutrient solution does not spill out of the reservoir. During the pumping process, be cautious as if pressure builds up, the water might overflow.
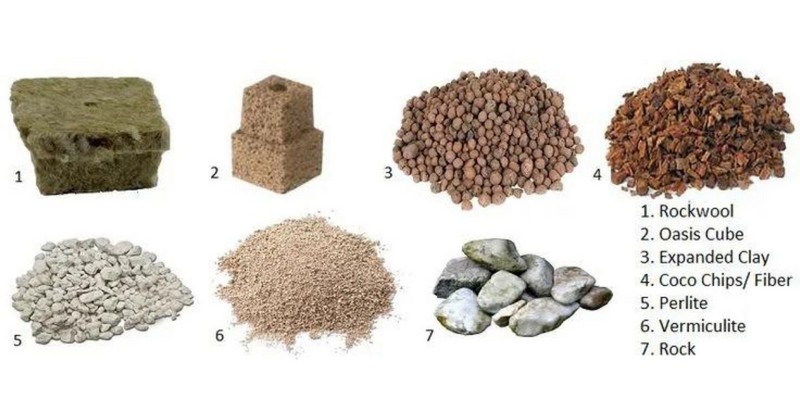
Growing Media
Because of how the system works, the growing media for ebb & flow must be firm enough not to be floated. We advise to buy some growing materials such as gravel, hydroton, perlite, and stone wool.

Other Materials
One benefit of the flood and drain system is that it is cost-effective. Additionally, it allows the improvisation of materials. You can use basic tools such as buckets, tubes, water bottles, trash cans, and storage totes as long as they can hold water.
Finding credible brands and high-quality materials for building a complete ebb and flow system is a big headache for many growers. No worries. With over 30 years of operation, Benchmark Hydroponics will offer the best hydroponic accessories to easily custom a DIY flood and drain system.
Different Types of Ebb and Flow Hydroponics
Various flood and drain structures use the same principle of water pumps to provide plants with nutrients.
Flooding Tray Design
The flooding train’s design differs from other models, as it only has one plant-growing container. The system includes a shallow rectangular or squared tray raised above the surface. The water reservoir is located underneath the container.
To flood the nutrients to the plants, one side of the tank allows water to flow in from the pool, while the opposite side allows water to move from the container into the nutrient solution reservoir.
The plants grow inside a plastic bucket on the flooding tray, and the seedlings in the bucket should include the appropriate growth media. The overflow tube controls the water level in the container, making it easier to transport the plant when needed.
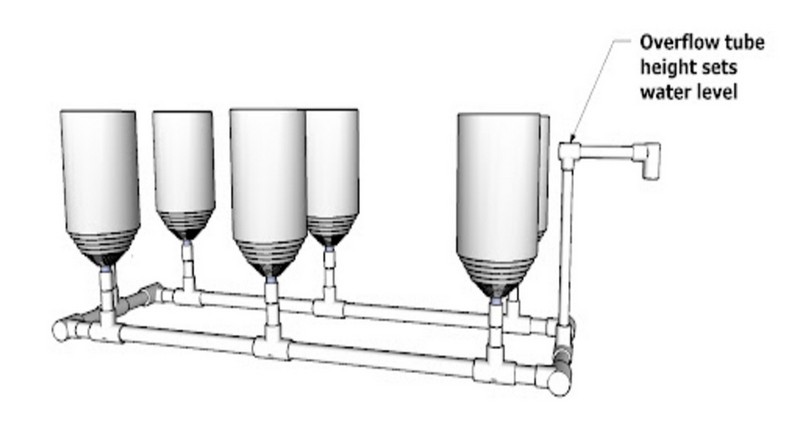
Containers in Series Design
An Ebb & Flow system with multiple buckets or containers can be set up creatively. Generally, several containers are connected through a single tube. The goal is to ensure that the nutrient flows reach all containers uniformly at the predetermined water level before being drained back to the reservoir via the tube.
Then, the pumps release nutrients evenly into all containers at once. Moreover, the containers' location must be higher than the water reservoir's so that the nutrient solution can return to the reservoir through gravity.
Let's look at popular designs with all containers in the Ebb and Flow series.
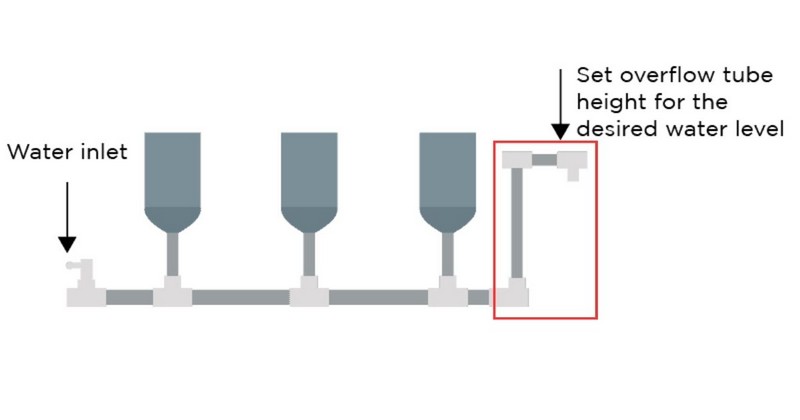
The Overflow Tube Height System
In the image below, the overflow tube is crucial in controlling the height of the nutrient solutions that pass through every container. It is also adjustable to fix the water level as quickly as possible.
The Surge Tank Ebb & Flow
Rather than relying on the overflow tube to get the water evenly in all containers, this design uses a primary tank (so-called surge tank) to distribute water equally in all containers.
It has a dual pump ebb & flow system. One pump moves the solution into the surge tank and all containers. Another one is in the surge tank to push the solution back to the reservoir.
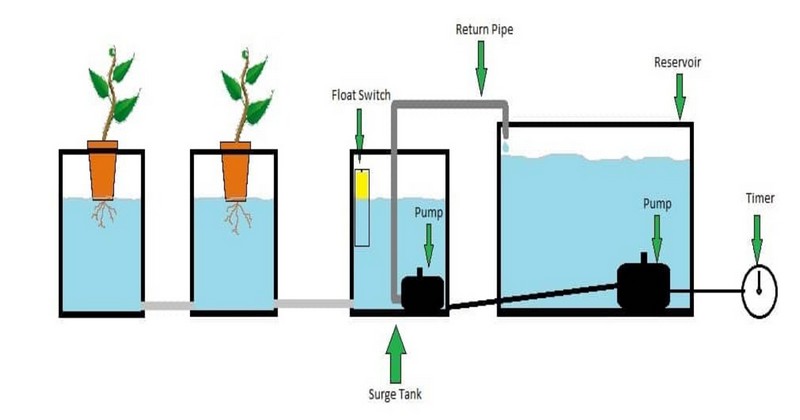
A submersible pump inside the surge tank helps push the nutrient solution back to the reservoir (a float valve in the surge tank turns on the pump inside it once the water reaches a certain level).
The Dutch Bucket
The Dutch bucket is a basic among the important parts of the ebb & flow system.
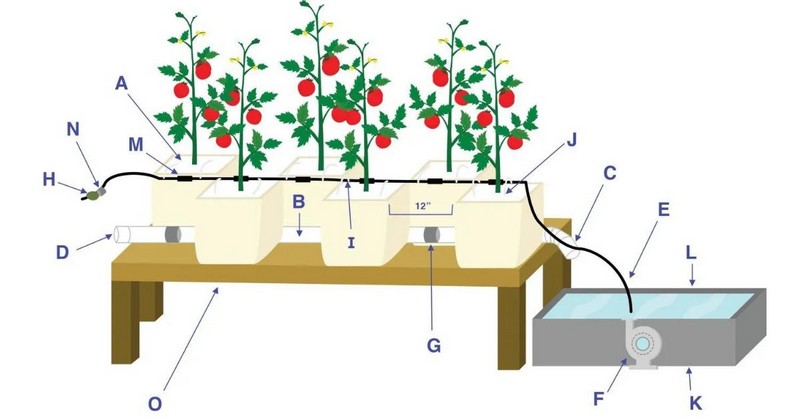
A Dutch bucket, or Bato bucket, is a hydroponic system in which 2 or more growing containers are attached with the same irrigation and drainage lines. This is an incredible water- and nutrient-efficient method, ideal for increasing heavy-feeding and vining plants like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants.
See more: hydroponics vs aeroponics.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ebb and Flow
Every hydroponics system has 2 sides, either to ebb and flow. Let's take advantage of the benefits and avoid the disadvantages mentioned below.
Advantages Of The Ebb And Flow
- Nutrient abundance for plants is present. The system ensures that your plants receive just enough nutrients. The overflow tube provides that flooding in the containers is not possible. Therefore, your plants become healthy and nutritious.
- Easy to install. Unlike other complicated types of Hydroponics, flood and drain do not require expert knowledge. After reading this post, you can quickly establish a stable and effective structure.
- Low cost. Setting up the structure, purchasing materials, and maintaining the fabric is affordable for everyone. Especially if you improvise the parts, you can save a lot of money.
- It is easy to use. Once you set up the system, the hard part of the job is over. The rest of the work is straightforward. The simple tasks are ensuring the availability of nutrient solutions and constant checking to confirm functionality.
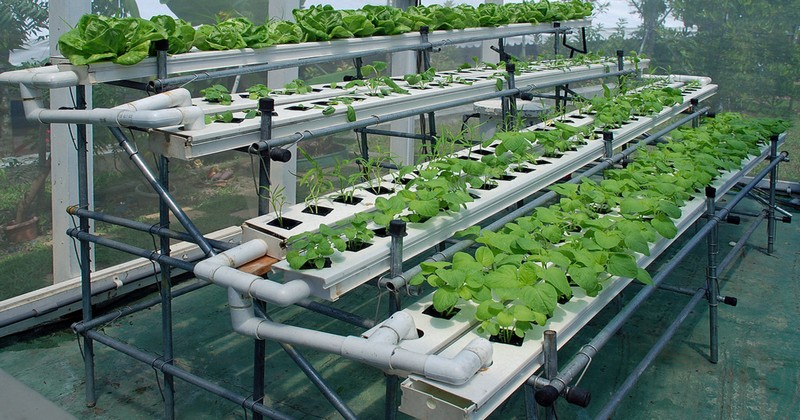

Disadvantages Of The Ebb And Flow
- Instances of unstable pH levels. Once the structure fails, the water overflows into the containers, thus flooding the plant. The excess nutrients create an unbearable PH environment that removes the farm produce.
- Breakdowns are a common issue. You must be extra careful once you decide to improvise the materials and set up your structure. Any small mistake in the formation may lead to the breakdown of the whole system..

As you can see, the flood and drain system is so effective, simple, and flexible, making it the best choice for beginners. Commercial growers have used Ebb & Flow to grow plants and fish for years and enjoyed significant results.
Hobbyists also find this system easy to install and enjoy fresh food in their indoor gardens. The ebb & flow is integral to the Hydroponic system and will stay. Visit Benchmark Hydroponics for more information!




