7 Types Of Hydroponics Systems (Expert Explained)
Hydroponics, a revolutionary method of growing plants without soil, has gained immense popularity recently thanks to its efficiency and ability to maximize crop yields. This comprehensive guide will show you the details of the 7 types of hydroponics systems.
Whether you're an hydroponics enthusiast or a beginner looking to explore this innovative cultivation technique, this expert guide aims to provide valuable insights of hydroponic systems.
Wick System
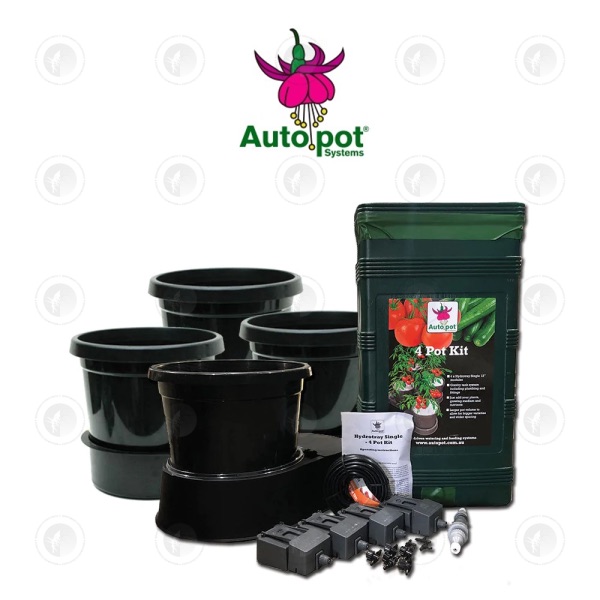

The Wick System operates like an autopot works. Water from a reservoir reaches the bottom of the Pot via tubing, and wicks upwards to the root zone.
It's a great starting point for anyone new to hydroponics, especially for growing hydroponic plants of all varieties.
Benefits
- Simplicity: The Wick System is one of the easiest hydroponic systems, making it easy for beginners to set up and maintain.
- Low Cost: The initial setup costs are relatively low since it doesn't require pumps or electricity.
- Low Maintenance: There are fewer components to manage, resulting in a system that requires minimal maintenance.
- Suitable for all scales of growth: Wick systems are well-suited for all scales, even on large commercial scale, or for hobbyist growers who want to experiment with different scales of hydroponics systems.
Drawbacks
- Limited Nutrient Control: The passive nature of the system may result in less precise control over nutrient delivery compared to more advanced hydroponic systems. And it can lead to salt buildup (from fertiliser).
- Monitoring Required: While the system is generally low-maintenance, regular monitoring of nutrient levels in the reservoir is necessary to ensure proper plant nutrition.
Water Culture
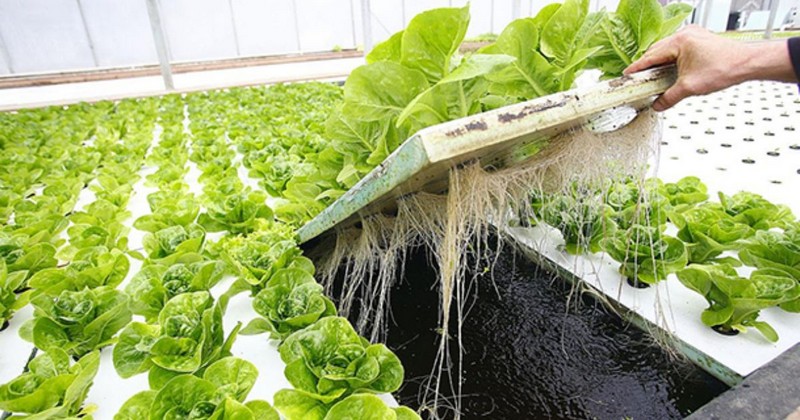

Water Culture, a simple among hydroponic systems types, suspends plant roots in a nutrient solution, offering continuous oxygen-rich conditions for optimal growth. Components include a reservoir for a balanced nutrient mix, a floating platform or ramp for plant support, and net pots for the growing medium.
Roots in the solution receive a constant nutrient supply, with the raft keeping plants buoyant and roots accessing water and oxygen. This direct exposure to air and nutrients ensures ample oxygenation, which is vital for plant metabolic processes.
Water Culture systems are a beginner-friendly introduction to hydroponics. They demonstrate the direct connection between nutrient-rich water and plant growth, making them a popular choice for easy and efficient soil-less cultivation.
Benefits
- Easiness: Water Culture systems are easy to set up and maintain. However, there might be some difficulties for beginners to start with.
- Direct Nutrient Access: Plants have immediate access to nutrients, promoting efficient nutrient absorption and fast growth.
- Cost-Effective: The system's simplicity often results in lower initial costs than more complex hydroponic setups.
Drawbacks
- Careful maintenance: In a water culture system, if you distract from caring for the plant, it can be at risk of root rot.
- Vulnerability to Power Outages: In a power outage, the lack of oxygenation to the roots can harm plant health.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
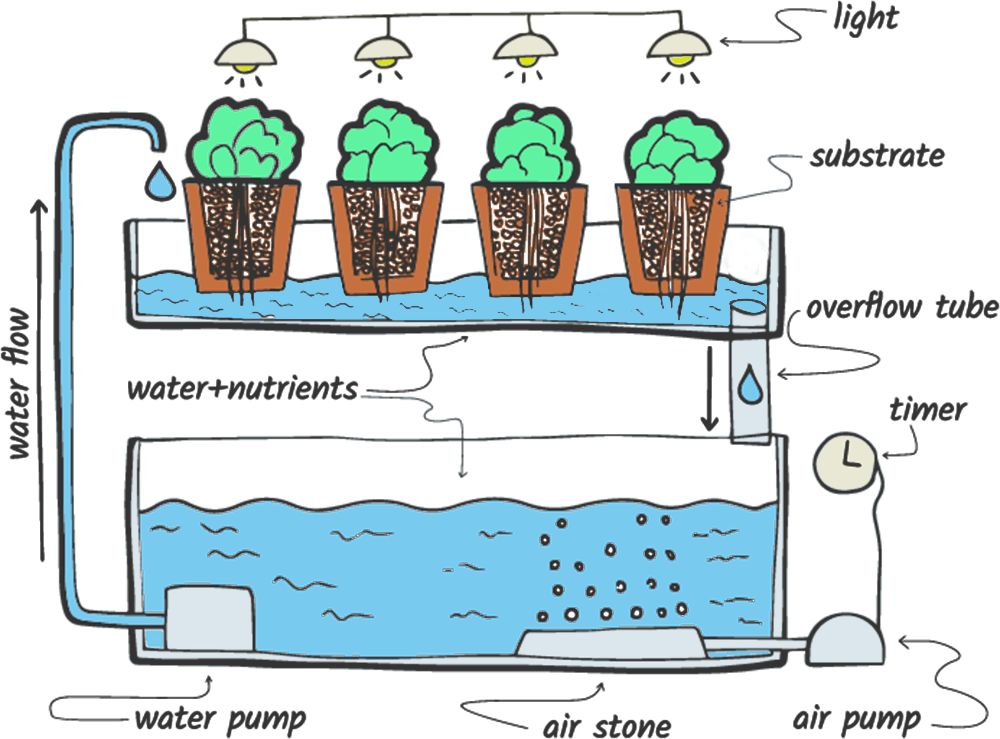
The Ebb and Flow hydroponic system intermittently floods and drains a growing medium, creating a dynamic environment for plant roots. Components include an increasing bed with a suitable medium, a nutrient reservoir, a submersible pump for flooding, and a timer for controlled cycles.
During the flooding phase, the nutrient solution is pumped into the bed and absorbed by the medium for nutrient delivery. In the draining phase, the solution recedes, creating air pockets for root oxygenation. This cyclical process, controlled by the timer, repeats, offering plants alternating access to nutrients and oxygen for optimal growth.
Benefits
- Nutrient Distribution: Provides even distribution of nutrients to plant roots.
- Oxygenation: Ensures adequate oxygenation of the root system.
- Versatility: Suitable for a variety of plants and growing mediums.
- Reduced Water Usage: Compared to continuous flow systems, the Ebb and Flow system can be more water-efficient
Drawbacks
- Complex Setup: Requires additional equipment and careful calibration.
- Potential for Equipment Failure: The system's reliance on a pump introduces the risk of failure.
Drip Systems
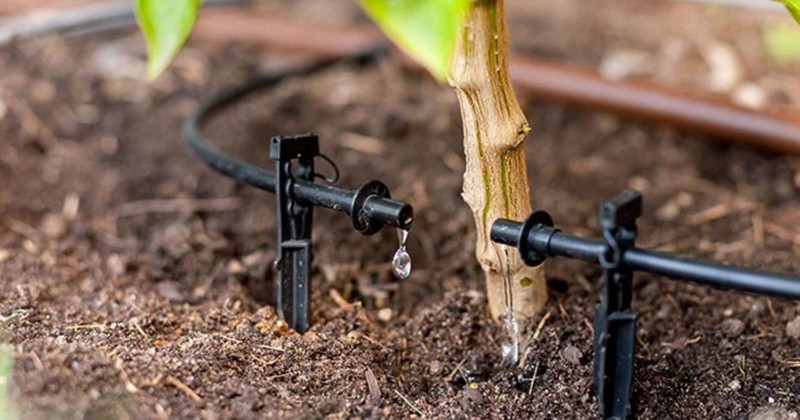

Drip systems in hydroponics deliver a carefully measured nutrient solution directly to each plant's base through tubes. The system includes a water pump for pressurizing the nutrient solution, tubing to distribute it, drippers releasing drops onto the growing medium, and a timer for controlled delivery. This method ensures plants receive consistent water and nutrients, fostering efficient and targeted growth.
The process involves pressurizing the nutrient solution with the pump, emitting drops onto the plants, allowing for controlled nutrient delivery, and either recirculating excess solution or draining it based on the system setup.
Benefits
- Precision: Provides precise control over nutrient delivery, minimizing waste and ensuring efficient use of resources.
- Versatility: Suitable for various growing mediums and adaptable to different crop types.
- Automation: Can be easily automated with timers, reducing the need for constant monitoring.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small-scale and large-scale hydroponic setups.
Drawbacks
- Clogging Concerns: Drippers or emitters may be prone to clogging, requiring regular maintenance.
- Uneven Distribution: Improper setup can lead to uneven nutrient distribution among plants.
Drip systems are widely used in hydroponics due to their efficiency and versatility, making them a popular choice for growers seeking controlled and automated nutrient delivery for their plants.
N.F.T. (Nutrient Film Technique)

N.F.T. (Nutrient Film Technique) is a hydroponic system with a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over plant roots. We place plants in sloped channels or gutters, and a pump lifts the nutrient solution to pour over the roots. Excess solution drains back for recirculation, ensuring continuous nutrient supply.
This efficient system promotes root absorption directly from the flowing solution, facilitated by gravity drainage. N.F.T. is known for its simplicity and is ideal for smaller plants with shallow root systems.
Benefits
- Efficient Nutrient Use: N.F.T. systems efficiently utilize nutrient solutions as they are continuously recycled.
- Reduced Water Usage: Compared to other hydroponic systems, N.F.T. systems can be more water-efficient.
- Ideal for Certain Crops: Well-suited for fast-growing, smaller plants with shallow root systems.
- Minimal Growing Medium: Since the roots are exposed and not embedded in a growing medium, there's less need for substrates.
Drawbacks
- Sensitivity to Disruptions: Any interruption in the flow of the nutrient film can quickly impact plant health.
- Challenges with Larger Plants: Larger plants with extensive root systems are likely to clog the NFT channels.
Aeroponic Systems

Aeroponic systems are particular hydroponic systems types where plants hang in the air, and their roots are in a nutrient-rich mist spraying. Aeroponics lets roots dangle freely, unlike other systems that immerse roots in water.
Essential parts include a growing chamber for plants, misting nozzles spraying nutrient mist, and a nutrient reservoir. During the misting cycle, roots absorb nutrients from the fog, getting oxygen as the mist droplets are fine enough to allow oxygen molecules from the surrounding air to dissolve into the solution. Excess mist is collected and reused in a continuous, efficient process.
Benefits
- Efficient Nutrient Absorption: Plants absorb nutrients directly from the mist, promoting rapid growth.
- Optimal Oxygenation: Frequent exposure to air ensures roots receive ample oxygen, enhancing plant health.
- Water Conservation: Aeroponic systems are known for their water efficiency compared to other hydroponic methods.
- Suitable for Various Crops: Aeroponics is versatile and can grow various plants.
Drawbacks
- Technical Complexity: Setting up and maintaining aeroponic systems can be more complex than other hydroponic systems.
- Sensitivity to Clogging: Misting nozzles can be prone to clogging, requiring regular maintenance.
The Kratky Method of Hydroponic
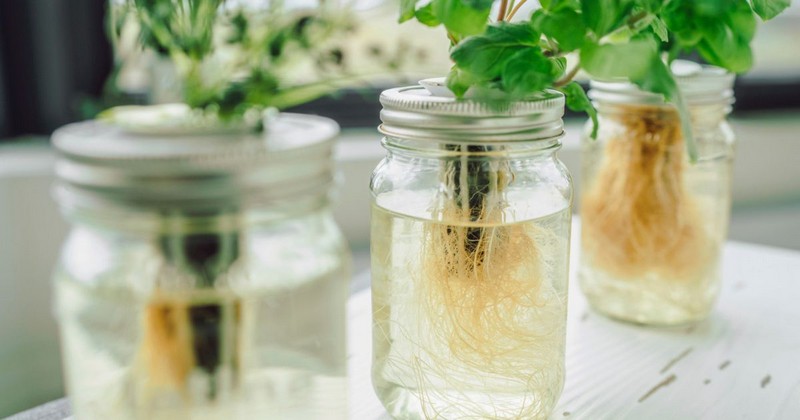

The Kratky Method is an easy hydroponic system Dr. Bernard A. Kratky created for growing smaller plants like leafy greens and herbs. It doesn't need electricity or pumps, making it simple and cost-effective.
Key components include a container holding the nutrient solution, a separate growing container with a growing medium, and an initial filling of the nutrient solution. As plants grow, they absorb the solution, and the water level decreases, exposing roots to air. Plants absorb nutrients passively until harvesting when the solution is exhausted.
Benefits
- Simplicity: The Kratky Method is straightforward and requires minimal equipment or maintenance.
- Low Cost: Since it doesn't need pumps or electricity, it is a cost-effective hydroponic solution.
- Suitable for Beginners: Easy for beginners to set up and manage due to its passive nature.
Drawbacks
- Limited to Certain Crops: Best suited for smaller plants and may be better for more extensive or fruiting crops.
- Not Continuous: The method relies on a finite nutrient solution, so it's not suitable for long-term or continuous growth
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of hydroponic systems for plant cultivation?
Hydroponic systems offer benefits such as faster plant growth, efficient nutrient use, water conservation, and growing plants in controlled environments.
How do Wick Systems work in hydroponics, and what are their advantages?
Basic wick systems use a wick to draw nutrient solution from a reservoir up to the plants' growing medium. This passive process ensures a steady supply of water and nutrients to the plants without pumps or electricity.
Advantages of Wick systems
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and maintain.
- Low Cost: Minimal equipment and energy requirements.
- Versatility: Suitable for various small-scale plants, while more advanced Wick Systems such as the Autopot are capable of cultivating larger-scale plants.
- Low Energy Consumption: No need for electricity.
- Quiet Operation: No noisy pumps.
Can you explain the simplicity and advantages of The Kratky Method in hydroponics?
The Kratky Method is a simple and low-cost way of hydroponics in growing plants without soil. You can place your plants in containers with a nutrient solution. As the plants use up the solution, the water level drops naturally.
What's great about it is that you don't need pumps or electricity, making it easy for beginners and those with limited resources. It's a hands-off approach that lets plants grow, making it a simple and efficient method, especially for growing plants like leafy greens and herbs.
Are there any common challenges or drawbacks associated with hydroponic gardening?
Yes, while hydroponic garden offers many advantages, there are also some common challenges and drawbacks associated with this cultivation method:
- Initial setup cost
- Technical complexity for beginners
- Dependency on a stable power supply
- Potential for disease spread
- Need for consistent monitoring and maintenance
- Issues with algae growth
- Reliance on technology
- The learning curve for nutrient management.
What hydroponic systems types are best for beginners, and how can one start hydroponic gardening?
Wick Systems and The Kratky Method are suitable types of hydroponic systems for beginners due to their simplicity. Getting started involves
- Understanding the chosen system
- Acquiring the necessary equipment
- Ensuring proper plant care.
As you step into the fascinating knowledge of hydroponics, understanding the nuances of different hydroponic systems is crucial for success. This expert guide has provided detailed insights into 7 types of hydroponics systems, offering a valuable resource for beginners and seasoned practitioners. With this knowledge, you can confidently do your hydroponic journey, unlocking the full potential of soil-less cultivation for optimal plant growth and bountiful harvests.




