How To Grow Hydroponic Plants in 5 Methods - Expert Guide For Beginners
Hydroponics frees plants from the dirt while still providing all the necessary nutrients for growth. Join us as we explore how to grow hydroponic plants and surpass traditional soil limitations. It's time to discover the magic of cultivating lush gardens without a soil bed – proof of the evolution of cultivation practices.
A Quick Guide to Hydroponics
- Hydroponics is a soil-less technique for growing plants, emphasising water-based nutrient solutions.
- Hydroponics systems enable year-round cultivation, overcoming seasonal limitations.
- Hydroponics consumes less water than traditional soil-based systems, making it more sustainable.
- It promotes accelerated plant growth and increased outcomes compared to traditional soil-based methods.
- This method is suitable for urban environments with limited space.
- We can set the hydroponic systems indoors and outdoors, with artificial lighting enhancing growth in indoor setups.
- The essential components include plants, containers, water, an anchoring system, nutrients, and light sources.
5 Hydroponic Grow Systems
Once you know why you would want to start growing with hydroponics, we want to introduce 5 types of grow systems. Each offers a unique approach to soil-less cultivation and upgrades your gardening experience.
1. Wick System
The wick system keeps hydroponics simple with no costly machinery or electrical gadgets. Many would use cotton wick when setting up this system at home because of its ease of installation and low material cost. Yet, for medium to large plants, it's not an ideal choice as it cannot deliver enough nutrients to support the needs of larger plants.
To solve this issue, use Autopot - which can grow almost anything. It is more aggressive, wicks quicker, and wicks more nutrient-solution at once. Don't know where to buy them? Look no further than Benchmark Hydroponics, your go-to source for hydroponic supplies in Melbourne.
Autopot Wicking Systems
However, if you still prefer a non-aggressive wick system for small plants, follow this instruction for a cotton wick system:
Project Metrics
- Working time: 15 minutes
- Total time: All year long with low-maintenance gardening
- Material cost: $35
What You'll Need
- A basin or bucket filled with water and hydroponic fertiliser.
- Cotton wicks are inserted into the growing tray.
- With holes for wicks, containing a seedling and a suitable growing medium (vermiculite, perlite, or soilless mixes).
- Incandescent lights are set up 24 inches from plants or adjusted accordingly for LED and fluorescent lights.
Detailed Instructions
Step 1: Set Up a Water Reservoir
- Create a reservoir in a basin with water and hydroponic fertiliser.
- Place the reservoir beneath the tray holding your plant and growing medium. (For the Autopot, the reservoir needs to be higher than the pot.)
Step 2: Connect Wicks to the Growing Tray
- Insert one or two wicks through holes in the bottom of the growing tray.
- Ensure wicks soak water from the reservoir and draw it up to the growing medium.
Step 3: Set Up a Growing Tray
- Place the growing medium in the tray above the water reservoir.
- Use a medium that utilises the capillary action of the wick effectively, such as vermiculite or perlite.
Step 4: Set Up a Light Fixture:
If using artificial light, set up an incandescent light fixture 24 inches from the plants.
2. Water Culture (Lettuce Raft) System
What is one of the easiest types of hydroponics system to set up? Many would answer the water culture system, commonly known as the lettuce raft system. Setting it up is a breeze – place your plants on a floating Styrofoam platform.
However, unlike the wick system, the water culture method requires a bit of water aeration through the raft system. Lettuce and spinach are the best vegetables to grow in this system.
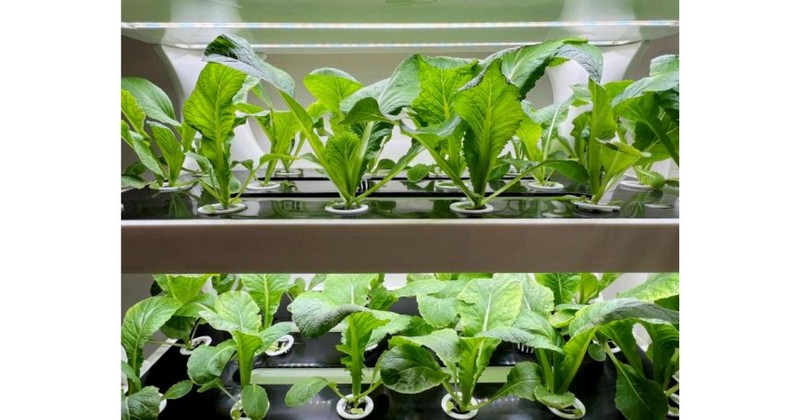

Water Culture (Lettuce Raft) System (Image Source: Food Network)
Project Metrics
- Working time: 45 minutes
- Total time: Add water-fertilizer solution when needed
- Material cost: $50 ($100 if you use a grow light)
What You'll Need
- Drill, rotary tool, or X-ACTO knife (optional)
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertiliser (dry or liquid)
- Styrofoam sheet
- Air stone and pump
- Seedlings in net pots with a growing medium
- Grow light (optional)
Detailed Instructions
Step 1: Set Up the Water Reservoir
- Fill an opaque container with water and hydroponic fertiliser based on your plant's characteristics.
- Use a container at least 12 inches deep, like an 80L Kitab Water Tank.
Step 2: Aerate the Water
- Introduce oxygen into the water using a common and affordable aeration system – an air stone and pump.
- Place the air stone in the water like those in home aquariums. Connect it to an external air pump, which releases tiny bubbles, infusing oxygen into the water.
Step 3: Set Up Your Growing Raft
- Prepare a floating Styrofoam platform tailored to fit snugly atop the reservoir.
- Cut holes in the platform to house net pots and plastic containers with perforated bottoms.
- Load the net pots with clay balls and seedlings. Ensure the roots make contact with the water in the reservoir.
Step 4: Place the Light Fixture
- Position a suitable fixture above the growing tray if relying on artificial light.
- Keep incandescent bulbs 24 inches from the plants. Adjust the height to 6 and 12 inches for LED and fluorescent lights, respectively.
3. Ebb and Flow System
Let's talk about the ebb and flow hydroponics system, also known as the flood and drain system. This system will add a touch of sophistication to your garden. Here's the breakdown:
Project Metrics
- Working time: Around 1 hour
- Total time: Refresh the water-fertilizer mix every week
- Material cost: $75 (or $125 if you use a grow light)
What You'll Need
- A bucket or basin for your water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertiliser (dry or liquid)
- Two tubes (a fill tube and a drain tube)
- A submersible pump
- An electronic timer
- A nifty growing tray
- A stand for that growing tray
- Seedlings in net pots with a growing medium
- A grow light if you want to amp up the brightness (optional)
Detailed Instructions
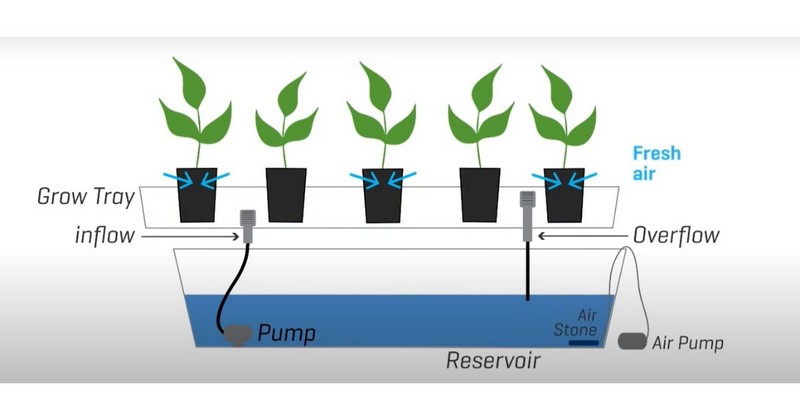
Ebb and Flow System (Image Source: Youtube)
Step 1: Set Up the Water Reservoir
- Place the reservoir beneath the flood tray's stand, filled with water and nutrient-rich fertiliser.
- Keep the nutrients fresh by changing the water every week.
Step 2: Connect a Fill Tube and Drain Tube
- Link the reservoir to the tray using fill and drain tubes.
- The fill tube connects to a submersible pump with a timer, controlling the water flow into the flood tray.
- A drain tube lets gravity do its thing, pulling water back for efficient reuse.
Step 3: Connect a Submersible Pump and Timer
- Use a submersible pump with a timer for precise watering control.
- Tailor watering frequency and duration to suit your plants' needs.
Step 4: Set Up the Flood Tray
- Positioned on a stand, the flood tray is a roomy, shallow haven for your plants.
- Grow your seedlings in perforated pots filled with a growing medium, like perlite. Make sure the pots are about twice as deep as the flood tray.
Step 5: Light It Up:
- Place a light system above the growing tray if natural light falls short.
- Adjust the height – 24 inches for incandescent bulbs or 6 and 12 inches for LED and fluorescent lights.
The ebb and flow system balances complexity and adaptability, creating the perfect environment for your plants to flourish. Therefore, learning how to grow hydroponic plants in this system is the first step to building a flourishing garden where your plants thrive.
4. Nutrient Film Technique
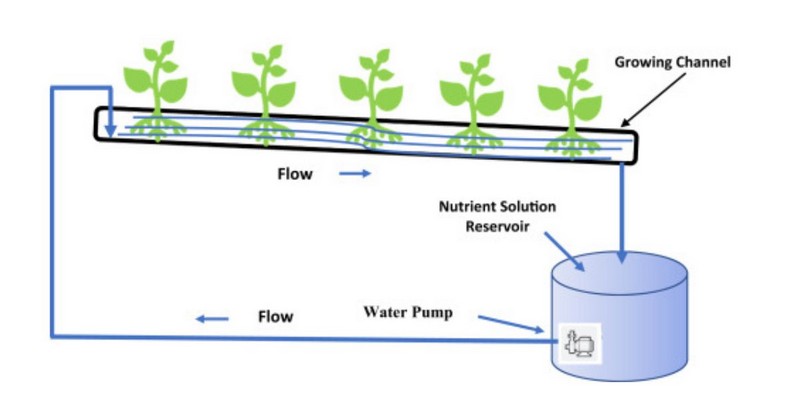
NFT in hydroponic growing (Image Source: ScienDirect)
The nutrient film technique (NFT) takes hydroponic gardening to a new level by maintaining a continuous flow of water-nutrient solution. It creates an optimal environment for plant roots to absorb nutrients. Let's dive into the workings of this dynamic system:
Project Metrics
- Working time: 1 hour
- Total time: Refresh the water fertiliser solution every week
- Material cost: $85 ($135 if you use a grow light)
What You'll Need
- Drill or rotary tool (optional)
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertiliser (dry or liquid)
- Two tubes (fill tube and drain tube)
- Air stone and pump
- Submersible pump
- Tube or PVC pipe to fit the seedlings
- Seedlings in net pots with growing medium
- Grow light (optional)
Detailed Instructions
Step 1: Set Up the Water Reservoir and Aeration
- Position the reservoir below the flood tray's stand, filled with nutrient-rich water.
- Insert an aeration bubbler into the reservoir to oxygenate the water.
Step 2: Connect the Fill Tube, Drain Tube, and Pump
- Connect the reservoir and the tray using fill and drain tubes.
- The submersible pump, connected to the fill tube, controls the continuous water flow into the nutrient film system.
- Unlike ebb and flow systems, there's no need for a timer as the water circulates non-stop.
Step 3: Set Up the Growing Tray
- Instead of a flat tray, NFT uses tubes or channels to guide the nutrient solution directly to the roots.
- Arrange the tubing at an angle, ensuring optimal nutrient flow. Use round tubes or PVC pipes with holes drilled for net pots or seedlings.
Step 4: Light It Up
- If natural light is insufficient, set up a light fixture above the growing tray.
- Keep incandescent bulbs 24 inches from the plants; LED and fluorescent lights can be placed 6 and 12 inches.
NFT thrives on a constant, nutrient-rich water flow, making it an excellent choice for fast-growing, shallow-rooted plants like lettuce, spinach, radishes, and herbs.
5. Aeroponic System
The advanced hydroponic system keeps plant roots in the air and mists them with nutrient solutions. While remarkably effective, this method demands sophisticated pumps and misters. Any equipment malfunction can lead to rapid dehydration and the swift death of plant roots.
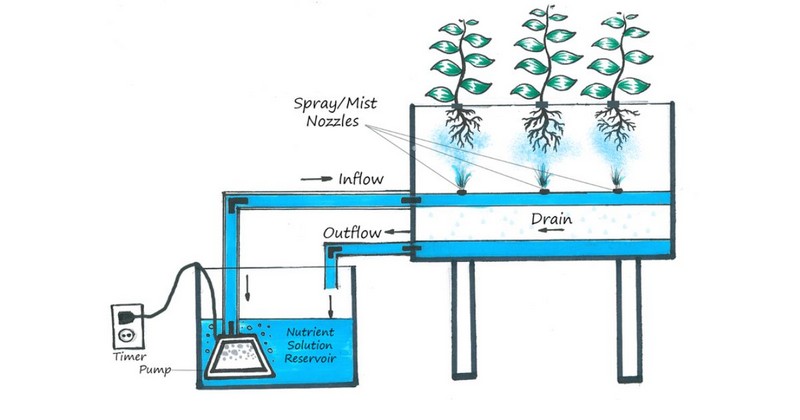
How Aeroponic system works (Image Source: Medium)
Project Metrics
- Working time: 1 hour
- Total time: Refresh the water fertiliser solution every week
- Material cost: $100 ($150 if you use a grow light)
What You'll Need
- Drill or rotary tool (optional)
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertiliser (dry or liquid)
- Submersible pump
- Spray tube
- Sprayer/misting head
- Tube or PVC pipe to fit the seedlings
- Seedlings in net pots and growing medium
- Grow light (optional)
Detailed Instructions
Step 1: Set Up a Water Reservoir with Aeration
- Place a container filled with nutrient-rich water under the growing chamber.
Step 2: Connect a Submersible Pump
- Link the reservoir to a mister or sprayer through tubing and a submersible pump.
- Direct the sprayer at the plant's roots, ensuring a consistent and precise misting experience.
Step 3: Set Up the Growing Chamber
- Create a setup with tubes or channels to suspend seedling roots evenly.
- This design optimises misting, allowing roots to absorb nutrients effectively.
Step 4: Set Up a Light Fixture
- Install a light fixture above the growing tray if natural light is lacking.
- Adjust the height for incandescent bulbs (24 inches) or LED and fluorescent lights (6-12 inches).
5 Hydroponic Growing Tips
Starting hydroponic gardening requires knowledge, budget, and patience. For beginners, learning how to make sure your water doesn't kill your plants is a critical first step. Let's explore crucial tips for a successful hydroponic garden:
Optimising Light and CO2
Giving your plants ample sunlight is a good practice to ensure their healthy growth. Each plant needs different amounts of sunlight at various stages of growth.
For example, some plants need 12 hours of sunlight for bud production. During the growth stage, it needs 18 hours of sunlight followed by 6 hours of darkness. So, implement a suitable timer for your lighting system to maintain consistent on/off cycles, promoting optimal growth.

A lighting system will promote optimal growth (Image Source: Stocking My Pantry).
Promote constant airflow with fans to enable carbon dioxide distribution. You can also attach carbon filters hydroponics to the fans to mask unwanted smells and enable carbon dioxide distribution.
Choosing the Right Lighting
High-intensity discharge (HID) light fixtures like the Philips Son-T-Light High-Pressure Sodium Lamp are ideal for hydroponic setups. Also, metal halide bulbs emit blue light and cater to plants in vegetative growth.
T5 lighting is another excellent option for small plants, seedlings, or clones, offering high-output fluorescence with minimal heat and energy consumption.
Temperature And Humidity Matters
Different plants require different temperatures; hence, you must research the specific plant to find out the proper temperature settings. Too high or too low temperatures can stunt plant development, and excessive water temperatures may lead to detrimental root rot. Hence, ideal temperatures will vary depending on which plant you're growing.
Besides temperature, keeping an ideal humidity in your hydroponic grow room is essential. Whether you grow vegetative or flower, humidity levels vary based on the type of plant and its growth stage. Remember, excessive moisture, especially in poorly ventilated spaces, can invite issues like powdery mildew.
Water Quality & pH Matters
Address the mineral content in your water, especially if it's high. Hard water with elevated minerals may slow nutrient dissolution. Consider filtering your water to enhance effectiveness.
Along with that, remember to maintain water pH levels between 5.8 and 6.2 for hydroponic gardening. Adjust pH using tools and chemicals if needed, ensuring the ideal slightly acidic environment.
pH meters & test kits
Choosing Your Hydroponic Crops
Opt for plants with shallow root systems for easier hydroponic cultivation. Herbs like basil, oregano, cilantro, and leafy greens like lettuce and kale are ideal for beginners. Then, you can experiment with larger crops like tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries as you gain experience.
Final Thoughts
We've explored diverse options for beginners and enthusiasts, from the simple Wick System to the intricate Aeroponic System. Each method offers a unique approach, and success lies in understanding, adapting, and nurturing. As you continue on this green adventure, follow us for more detailed instructions on how to grow hydroponic plants.




