How To Propagate A Peach Tree: Effective Methods for Beginners
Knowing how to propagate a peach tree properly ensures healthy growth and bountiful harvests for years. Therefore, you need Benchmark Hydroponics' step-by-step guidelines to propagate your peach plants successfully. So, let's dive in and see how we bring your dream garden into reality.
Table of Contents
Why Try Propagating Peach Trees From Cuttings?
We can grow peach trees from seeds, cuttings (using hardwood cuttings), grafting, or budding. However, commercial farmers typically choose grafting or budding because they bring purity, high success rates, overall plant health, and early fruit production.
What makes peach trees special is they are one of the few fruit trees we can also propagate from softwood cuttings. It is the process of using fresh growth stems from the tree.
Typically, peach trees are propagated through grafting rather than cuttings.
Grafting means cutting two healthy trees, merging them, and then binding them together so that one variety grows on the rootstock of another.
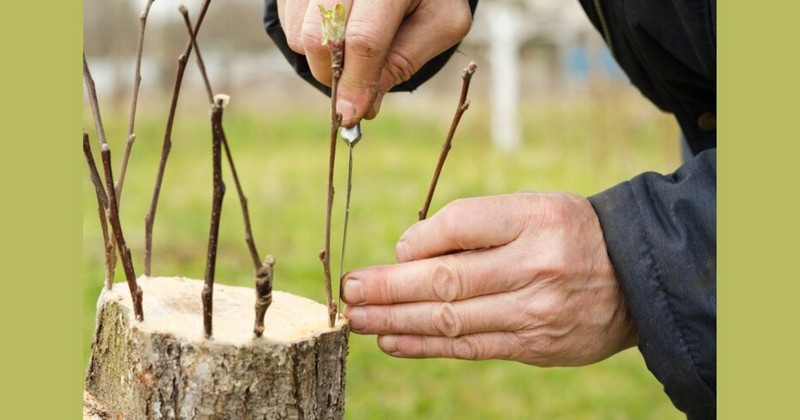

Grafting method
Grafting allows farmers to combine the strength of a strong rootstock with the desired traits from the top graft (even if it reduces the fruit's natural sweetness).
Notices Before Propagating Peach Trees
Before propagating peach trees, here are some things you should consider to achieve the best results:
- Choosing Your Grafting Pair: Get a rootstock and a scion from a healthy peach tree. The rootstock should resist diseases, while the scion should come from a mature and thriving branch.
- Best Times for Cuttings: April is an ideal time to start rooting softwood or stem cuttings from trees as they experience better growth and are more receptive to rooting.
- Plant Patents: Many peach tree varieties are protected by the plant patent. In these cases, you need permission from the patent holder before propagation. Propagation may not be allowed without proper authorisation, or you must pay royalties.
- Testing for Pathogens: If using your bud sources, consider testing them for viral pathogens. This testing is costly, ranging from several hundred to over $500, depending on the lab, the number of virus types tested, and the testing method.
How To Propagate A Peach Tree?
As mentioned above, gardeners can propagate peach trees using different methods, each with unique features and processes. Let's dive further and see which way should you apply to your tree:
1. Grafting
Many plants and trees can be grafted, including fruit trees like peach, cherry, and fig and other trees like beech, spruce, etc. Farmers commonly start grafting in late fall or winter or in early spring. The ideal temperature for this propagation method is 75-80 degrees Celsius.
Prepare the following materials and tools:
- Sharp knife
- Grafting tape
- Wax or other decomposable material
- Scion material
- Rootstock material
But how are peaches propagated using the grafting method? Here's how:
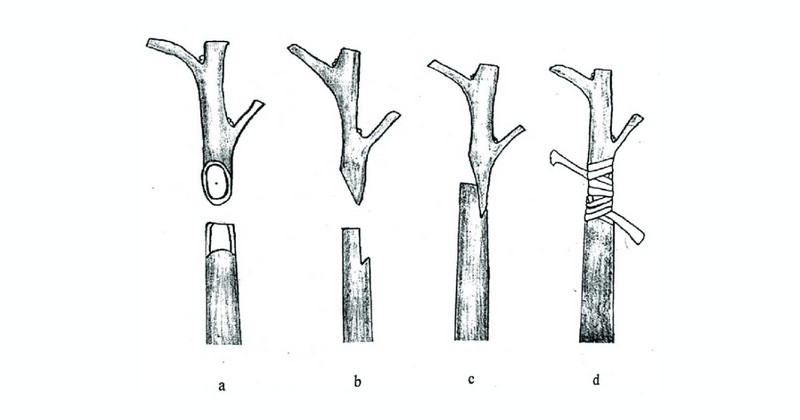
Steps to graft a peach tree
Step 1: Select and Prepare Rootstock
Choose rootstock adapted to local conditions, healthy in appearance, and compatible with the grafted variety.
Find scaffolding branches about 1-2 inches in diameter and cut them finely. You can also use the main stem as a stock branch.
Step 2: Split the Collar Branch
Using a sharp knife, split the collar branch's cut end about 1 1/2 inches deep.
Step 3: Prepare the Scion
The scion wood should be:
- Disease-free
- 1/4 to 1/2 inch in diameter
- Have at least three buds
- Between 2-8 inches long.
Keep the scion moist before grafting to prevent it from drying out.
Step 4: Cut Downwards the Scion
Use the prepared knife to cut downwards on both sides of the scion's base to create a wedge shape.
Step 5: Insert the Scion Wedge
Pry open the split on the rootstock and insert the scion wedge, carefully aligning the cambiums of both the scion and the rootstock.
Step 6: Cover the Wound
Wrap the grafted area with the chosen decomposable material to keep excess water out and prevent drying. Be careful not to wrap it too tightly.
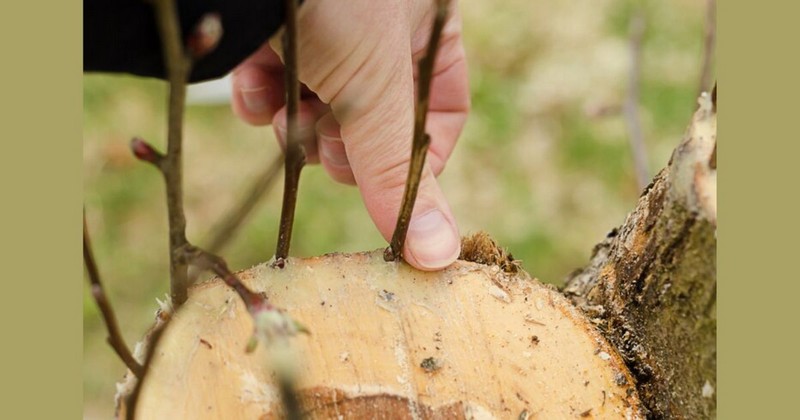

After propagating, monitor the graft daily and remove any insects around the area. Stabilise the newly grafted branch to prevent damage by the wind as it grows.
See more: How to propagate plants in water
2. T-Budding
Gardeners typically do T-budding when the tree's bark easily separates in late spring or summer. It's also known as June Budding and works well in regions with long growing seasons.
To begin, prepare beforehand the following materials and tools:
- Sharp knife
- A grafting rubber or a rubber band
- Parafilm
- Rootstock material
- Budwood material
Here is how to propagate a peach tree using the T-budding method:
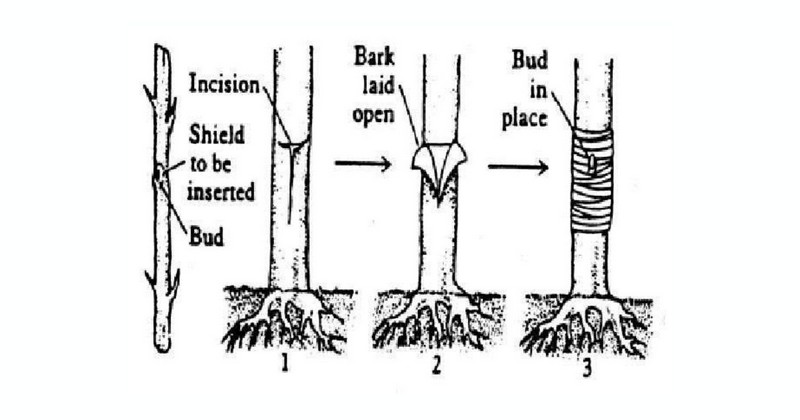
Steps to T-bud a peach tree
Step 1: Prepare the Rootstock and Budwood
- Get peach rootstock from a nursery or grow from seed. Pay attention to desirable traits like dwarfing effects or disease resistance.
- Choose healthy budwoods with good fruit production.
- Choose a long, healthy branch with 5-8 buds from the current season's growth.
After the preparation, cut the budwoods immediately and store them in a plastic or burlap bag with water moss to avoid drying out.
Step 2: Create a T-cut
Choose a flat and smooth area on the rootstock's bark. Make a horizontal slit followed by a perpendicular cut to form a "T" shape, exposing the vascular cambium.
Step 3: Prepare and Insert Bud
Remove leaves without damaging the buds. Make a scraping cut under the bud that matches the size of the T-cut in the rootstock.
Then, insert the bud into the T-shaped pocket of the rootstock, ensuring maximum contact between cambiums.
Step 4: Protect the Graft Union
Then, wrap a piece of parafilm around the graft union to waterproof it. Don't cover more than one layer of film above the bud.
And you've done it! About two weeks after budding, cut the rootstock about two inches above the graft union to break apical dominance and force bud growth. Use a metal stake to promote vertical growth if needed.
Also, watch for signs of systemic illness or pathogens. If there are problems, such as incompatible compounds, promptly take the necessary actions to resolve them.
3. Cuttings
Plant cloning, cutting, or striking are different terms for describing the propagation method of creating new plants from existing ones.
To propagate a peach tree, let's try softwood cuttings. Here's all you need:
- Pot
- Potting soil
- Plastic bag
- Rooting hormone powder
- Pruners
- Knife (such as an X-acto knife)
- Parent plant
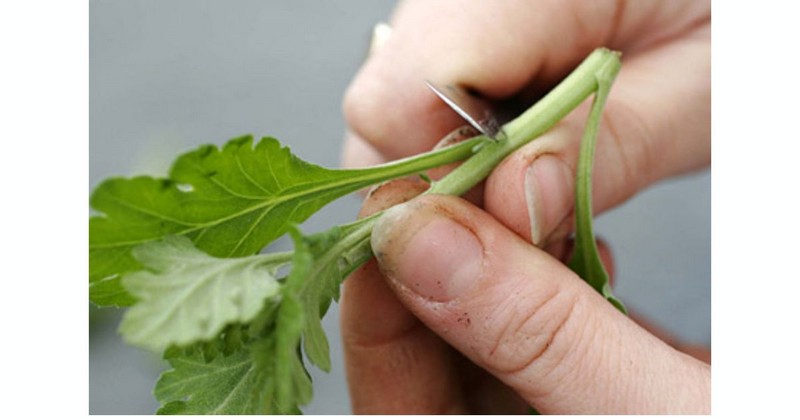

An example of softwood cuttings
Step 1: Sterilize Your Pot
Before starting, ensure the pot is free of microorganisms that could hinder the rooting process. Clean the pot thoroughly with water, then bathe it in 1 part bleach and 9 parts water for 20 minutes. Rinse the pot and let it air dry.
Meanwhile, clean and sterilise any other tools you'll be using.
Step 2: Take Your Cuttings
The question is: How do you take cuttings from a tree? We need cuttings with fresh growth, about 4 to 6 inches long. Cut them at an angle just above the nodule or joint on the stem.
Keep the cuttings moist by wrapping the cut stems in wet paper towels until ready for planting.
Step 3: Prepare the Stems
The next step is to prepare the stems for rooting:
- Remove any leaves that will be below the soil level.
- Use an X-acto knife to scrape off some of the bark from the cut end of the stem, then cut the tip at an angle.
Step 4: Soak the Cut Stems in Rooting Hormone
Soak the cut ends of the stems with rooting hormone powder to boost root growth. You can dip the stems into the powder or roll them in after placing some on a dish or paper towel.
Step 5: Put Stems Into The Pot
Place the stem with the cut side down. Apply the powder downwards into a pot filled with sterile potting soil.
We recommend rooting more cuttings than necessary to avoid possible failures.
Step 6: Water and Provide Humidity
Finally, water the cuttings thoroughly and place the pot on a tray in a place with full natural sunlight.
This process is similar to how to propagate money trees, pine trees, etc. After cutting, use the prepared plastic bag to cover the pot to create a humid environment. Then, open the lid daily to water and circulate air.
How Do You Know If The Peach Tree Cuttings Have Rooted?
We can recognise the successful rooting of peach cuttings through the new growth that appears from the cuttings. You will see the development of tiny leaves and a healthy, vibrant appearance in the stem.
Contrarily, if the cuttings fail to root, you will see signs of damage. For example, the leaves will turn deep brown or black, eventually falling off, and the stems will become more brittle.
Then, what to do with the rooted cuttings? Once your cuttings have successfully implanted, the next phase is to move each cutting into its own pot. This action allows them to grow and enhance a healthy root system.
To grow outdoors, you can transplant rooted cuttings into the garden in the fall, ensuring they receive enough water to grow well. Alternatively, keep the houseplant for another year. Then, wait for the following spring to transplant them into the outdoors.\
See more: How do you propagate pine trees?
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you grow a peach tree from a cutting?
Yes, you can grow peach trees from a cutting. With proper care and suitable growing conditions, these cuttings can develop roots and become healthy peach trees over time.
Should I cut the top of my peach tree?
Yes, but don't prune too high above the ground. The tallest branch of the peach tree should be about 30 inches above the ground. Instead, prune any branches taller than 30 inches.
The Bottom Line
Learning how to propagate a peach tree demands time, money, and effort, but the result is worth it. We may fail a few times, but with enough practice and experience, you will successfully create your dream garden. Follow us for more exciting and helpful content for your garden.




